【学校训练记录】10月个人训练赛3个人题解
A:

根据题意我们可知,第一种事件为从1到i的和,第二种事件为从y到i的和故我们可以通过前缀和来保存从i到i+1所化的时间。再遍历寻找最小值即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl "\n"
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n, a[1010];
void solve(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n-1; i++){
string s; cin >> s;
if(s == "Patrik"){
int x; cin >> x;
a[i] = x;
}
else {
int x, y; cin >> x >> y;
a[i] = a[x-1]+y;
}
}
int mins = 1e18;
for(int i = 1; i <= n-1; i++){
mins = min(mins, a[i]-a[i-1]);
}
for(int i = 1;i <= n-1; i++){
if(a[i]-a[i-1]==mins){
cout << a[i]-a[i-1] << ' ' << i << ' ' << i+1 ;
break;
}
}
}
signed main (){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
// cin >> T;
T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
B:
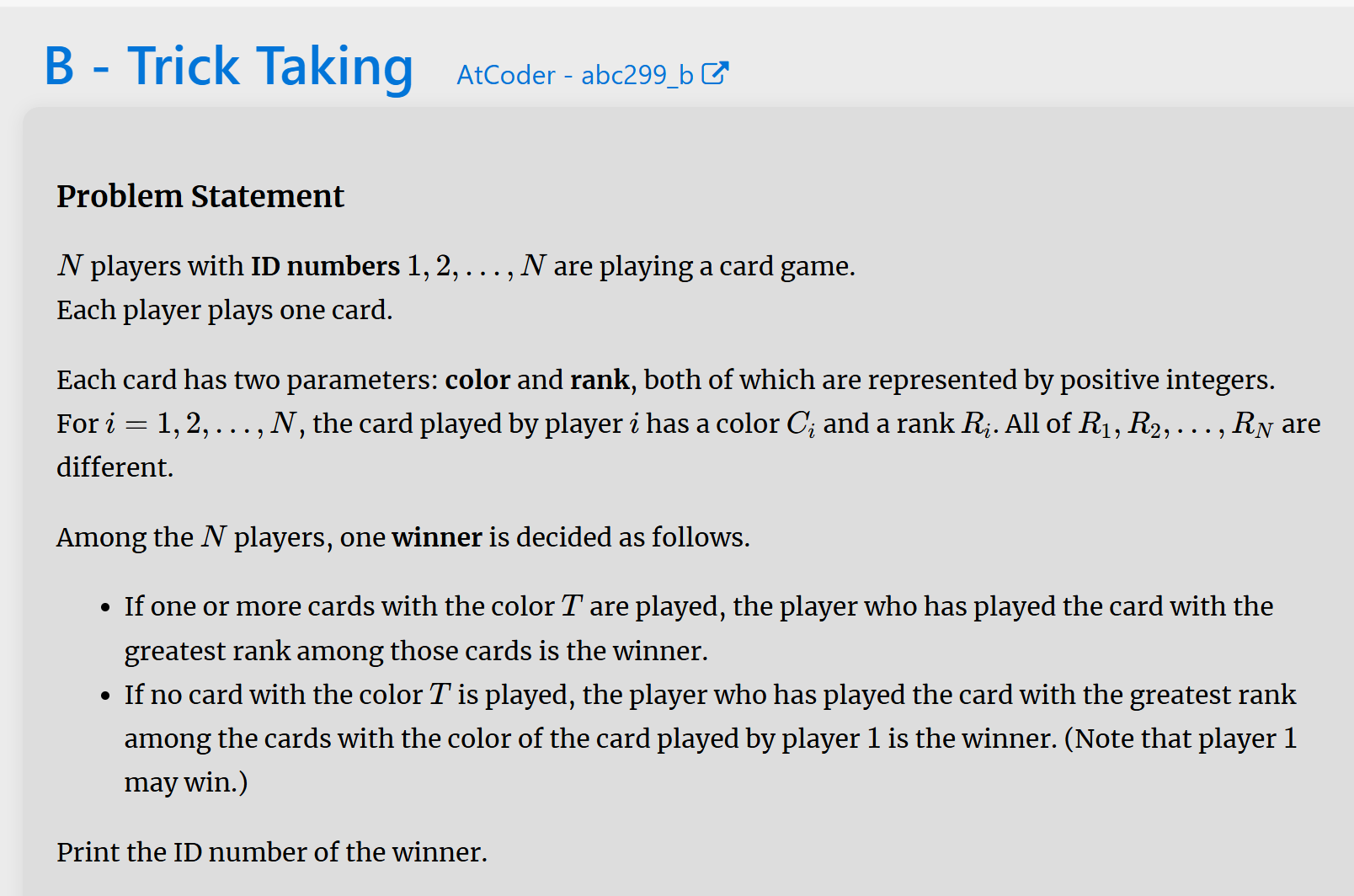
每人一张牌,每人手中的牌有一个权值,若牌与T相同则为找出其权值最大,没有T就找与第一个人相同且权值最大的即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl "\n"
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n, m, a[200010], b[200010];
void solve(){
cin >> n >> m;
int maxs = 0, num = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> b[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(a[i]==m && b[i]>maxs){
maxs = b[i];
num = i;
}
}
if(!num){
m = a[1], maxs = b[1], num = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(a[i]==m && b[i]>maxs){
maxs = b[i];
num = i;
}
}
}
cout << num;
}
signed main (){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
// cin >> T;
T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
C:
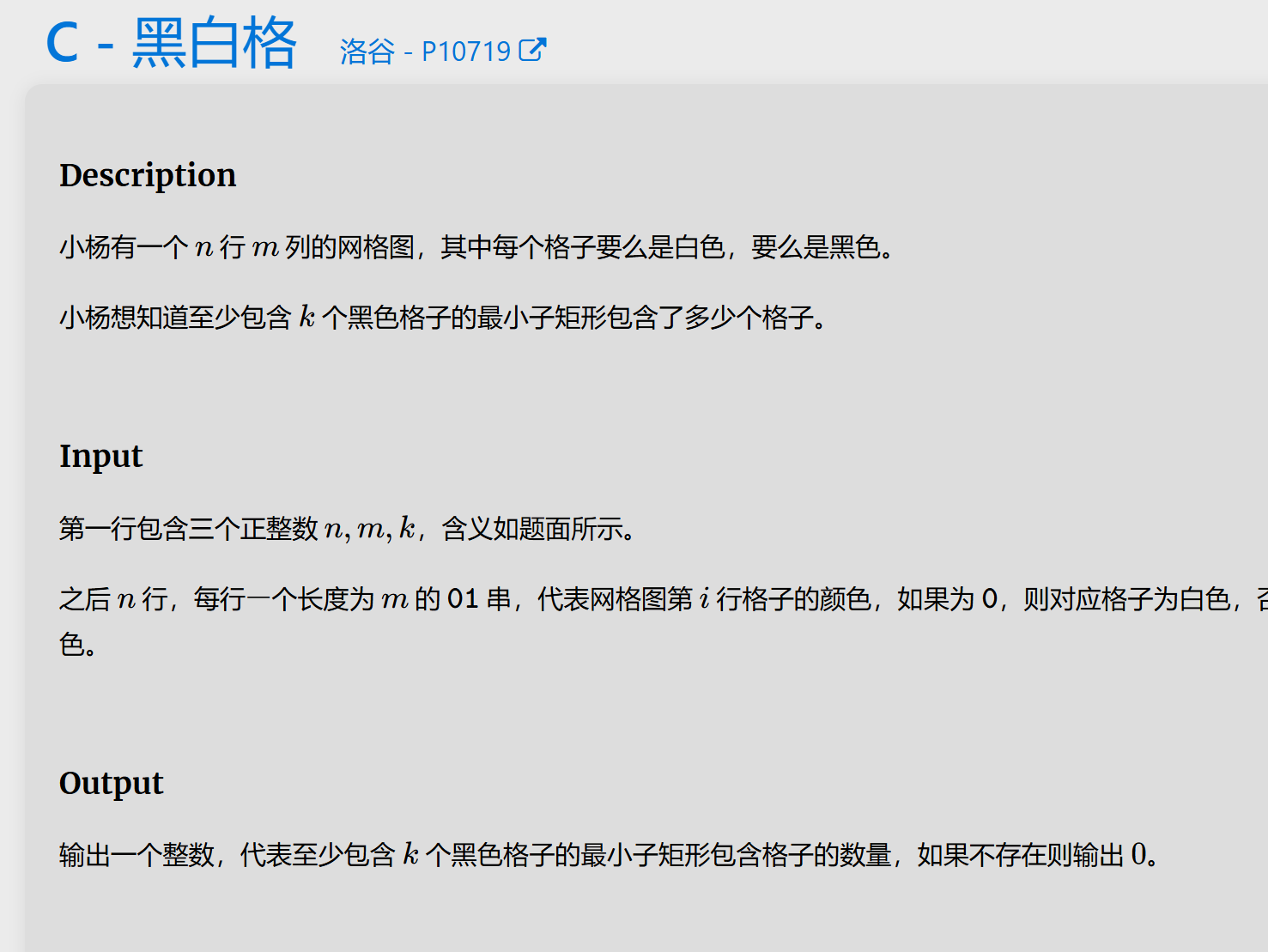
此题根据求和不难想到为二维前缀和,而数据量较小,我们可以直接遍历矩形左上和右下的端点来遍历每一个矩阵即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl "\n"
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n, m, k, a[110][110];
void solve(){
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
char ch; cin >> ch;
int c = ch-'0';
a[i][j]= c-a[i-1][j-1]+a[i-1][j]+a[i][j-1];
}
}
int mins = 1e18;
for(int x = 1; x <= n; x++){
for(int y = 1; y <= m; y++){
for(int i = x; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = y; j <= m; j++){
int now = a[i][j]-a[i][y-1]-a[x-1][j]+a[x-1][y-1];
if(now>=k) mins = min(mins, (i-x+1)*(j-y+1));
}
}
}
}
if(mins == 1e18) cout << '0';
else cout << mins;
}
signed main (){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
// cin >> T;
T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
D:

数据量小我们可以直接遍历每一种范围内位置的左端点并计算实现不交税之后的值,求出其最小值
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl "\n"
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n,a[1100];
void solve(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
sort(a+1, a+1+n);
int sum = 1e18;
for(int i = a[1]; i <= a[n]; i++){
int now = 0;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
if(a[j]>i+17){
now+=(a[j]-i-17)*(a[j]-i-17);
}
else if(a[j]<i){
now+=(i-a[j])*(i-a[j]);
}
}
sum = min(now, sum);
}
cout << sum;
}
signed main (){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
// cin >> T;
T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
E:
题目可以分为两部分,一部分求y值,第二部分求是否可以完成平分。对于第一部分,我们通过并查集将其i,j相连,其根节点为首都(0,0)然后通过while来记录到达首都的步数,将其加一存入数组,第二部分,要将其分为两个相等的值,若sum不为偶数,一定不行,而如果是偶数,我们可以只选出和为sum/2的部分,而另一部分,也一定sum/2,这对于每个数都只有选或不选,故使用01背包,若背包刚好装满,即为可以平分。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl "\n"
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n, a[510], b[510], c[510], d[510], dp[200010];
int dis(int x, int y){
return (a[x]-a[y])*(a[x]-a[y])+(b[x]-b[y])*(b[x]-b[y]);
}
void solve(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) c[i] = 1e18;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i] >> b[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int p = 1;
for(int j = 0; j <= n; j++){
if(i!=j){
if(dis(j, 0)<=dis(i, 0) && dis(i,j)<c[i]){
c[i] = dis(i,j);
d[i] = j;
p = 0;
}
}
}
if(p) d[i] = 0;
}
int sum = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x = i;
int num = 1;
while(d[x] != 0){
num++;
x = d[x];
}
a[i] = num+1;
sum+=a[i];
}
a[0] = 1;
if(sum%2==1){
cout << "No";
return ;
}
// for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++) cout << a[i] << ' ';
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = sum/2; j >= a[i]; j--){
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j-a[i]]+a[i]);
}
}
if(dp[sum/2] != sum/2) cout << "No";
else cout << "Yes";
}
signed main (){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
// cin >> T;
T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
0
F:

区间dp通过计算i到i+l的区间内的最优解来依次实现每个区间的最优解,直到大小为整个区间,其中a[i][i+l]为从i开始长度为l的区间的最优解,其中遍历实现依次将区间内哪两个操作过的史莱姆合成值最小
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl "\n"
#define int long long
using namespace std;
int n, a[410], b[410][410], c[410];
void solve(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i], c[i]=c[i-1]+a[i];
for(int l = 1; l <= n-1; l++){
for(int i = 1; i+l <= n; i++){
b[i][i+l] = 1e18;
for(int j = 1; j <= l;j++){
b[i][i+l] = min(b[i][i+l-j]+b[i+l-j+1][i+l],b[i][i+l]);
}
b[i][i+l]+=c[i+l]-c[i-1];
// cout << b[i][i+l] << ' ' << i << ' ' << i+l << endl;
}
}
cout << b[1][n];
}
signed main (){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
// cin >> T;
T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}