cf_补题计划_Edu_163_DE
D. Tandem Repeats?
呃
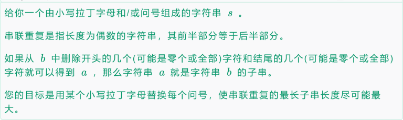

从复杂度来说,可以进行\(n^2\)的操作,呃因为是子串数量级也是\(n^2\),考虑是否子串之间可以相互转移,这个很类似求最长回文串(对于最长回文串我们枚举中点,向外延申即可,因为对于同一个中心可以转移),而对于串联重复串,前一部分等于后一部分,我们可以考虑固定长度,那么长度一样的字串就可以转移。
跟回文串的处理差不多
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define pb push_back
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define all(a) a.begin(), a.end()
#define debug(x) cout << #x << " = " << x << endl
#define sz(a) ((int)a.size())
const int mod = 998244353, N = 505, G = 3;
void solve()
{
ll ans = 0, n;
string a;
cin >> a;
n = a.length();
a = ' ' + a;
for (ll k = n; k >=1; k--)
{
ll sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i + k <= n; i++)
{
if (a[i] == a[i + k] || a[i] == '?' || a[i + k] == '?')//如果相等就+1
sum++;
else
sum = 0;
if (sum >= k){
cout << k * 2 << endl;
return;
}
}
}
cout << 0 << endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
E. Clique Partition


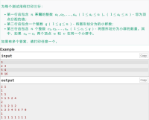
呃,大概意思是将n个数,每个数给个数,然后在把他们分成m块,每块里面满足\(|i-j|+|a_i-a_j|<=k\),然后让m尽可能的小。
然后我们发现i,j尽量的越接近会让|i-j|+|a_i-a_j|更小,更容易满足小于等于k的要求,所以每块的选取应该是连续的,然后大力guess
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define pb push_back
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define all(a) a.begin(), a.end()
#define debug(x) cout << #x << " = " << x << endl
#define sz(a) ((int)a.size())
const int mod = 998244353, N = 2e5 + 10, G = 3;
ll d[N], c[N];
void solve()
{
ll n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
d[i] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
c[i] = (i - 1) / k + 1;
d[c[i]]++;
}
ll sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (c[i] != c[i - 1])
sum = 0;
sum++;
if (sum <= d[c[i]] / 2)
cout << (c[i] - 1) * 2 * k + 1 + d[c[i]] / 2 - i << ' ';
else
cout << (c[i] - 1) * 2 * k + 1 + d[c[i]] / 2 + d[c[i]] - i << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
cout << (n - 1) / k + 1 << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << c[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}